AP Syllabus focus:
‘Federal agencies exercising discretion include the Department of Homeland Security, Transportation, Veterans Affairs, Education, the EPA, the FEC, and the SEC, each regulating different policy areas.’
Regulatory policy is often made through agencies that turn broad statutory goals into detailed, enforceable rules. Knowing which agencies regulate which policy areas helps you track where policy disputes actually get decided.
What “key rulemaking agencies” means
Agencies matter because they combine specialised expertise with discretion to set binding requirements within their policy domains.
Rulemaking: The process by which a federal agency issues regulations (rules) that implement and interpret laws, creating specific standards that can be enforced.
Rulemaking shapes daily life by setting eligibility standards, safety thresholds, reporting requirements, and penalties—often with significant political controversy.
Executive departments with major regulatory roles
Many high-impact rules come from cabinet-level departments. Their regulations typically govern large, complex systems (security, transport, education, benefits).
Department of Homeland Security (DHS): security and immigration administration
DHS regulates and administers policies tied to national security and border management.
Policy areas commonly shaped by DHS rules:
Aviation and transportation security standards (screening procedures, security requirements)
Immigration processing and compliance requirements (documentation, procedures, enforcement priorities)
Cybersecurity and infrastructure protection guidance that can become enforceable standards in specific contexts
Key idea for AP Gov: DHS rules often reflect tension between civil liberties concerns and public safety priorities, especially when agencies must respond quickly to emerging threats.
Department of Transportation (DOT): transportation safety and infrastructure regulation
DOT issues regulations that standardise safety and operational practices across transportation networks.
Policy areas commonly shaped by DOT rules:
Vehicle safety requirements and performance standards
Air travel safety regulations and operational compliance
Hazardous materials transport standards (labelling, routing, handling rules)
DOT rulemaking illustrates how Congress can set broad goals (safe travel; efficient commerce) while agencies define the technical thresholds and compliance details.
Department of Veterans Affairs (VA): benefits administration and healthcare standards
The VA regulates how veterans’ benefits and services are delivered.
Policy areas commonly shaped by VA rules:
Eligibility criteria for benefits and services
Disability ratings and evidence requirements
Healthcare system administration rules for VA facilities and programs
Because the VA serves a defined population, its regulations often focus on procedural fairness, consistency, and the administrative capacity to implement Congress’s benefit promises.
Department of Education: schooling policy implementation through conditions and compliance
The Department of Education shapes education policy largely through administrative rules tied to federal programs.
Policy areas commonly shaped by Education Department rules:
Student aid and programme eligibility requirements
Civil rights compliance standards tied to federal education funding
Accountability and reporting requirements for institutions receiving federal funds
Education rulemaking often operates through “if you take federal money, you must comply,” making regulations a central tool for influencing schools and universities.
Independent regulatory commissions and specialised regulators
Some agencies are designed to be more insulated from direct presidential control, focusing on elections and markets.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): environmental and public health regulation
The EPA issues rules that limit pollution and manage environmental risk.
Policy areas commonly shaped by EPA rules:
Air and water quality standards
Emissions limits for industries and (in coordination with other authorities) transportation sources
Chemical safety and hazardous waste management requirements
EPA rules often require technical judgments (acceptable risk; measurement methods), making agency expertise central and litigation common when affected industries or states challenge regulations.
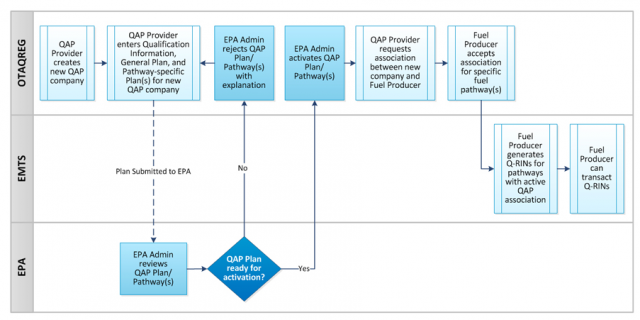
This EPA process diagram models a real-world compliance workflow: outside entities submit required information, the agency reviews it, and an approval decision activates enforceable participation in a regulatory program. It illustrates how agencies translate statutory authority into administrative steps (submission, review, approval/denial, and ongoing regulated activity) that structure compliance. In AP Gov terms, it’s a concrete example of bureaucratic discretion operating through procedures. Source
Federal Election Commission (FEC): campaign finance and election-related compliance
The FEC regulates campaign finance to administer and enforce federal election law.
Policy areas commonly shaped by FEC rules:
Contribution and expenditure reporting requirements
Disclosure rules for political committees and campaign spending
Enforcement procedures (investigations, penalties, advisory opinions)
FEC rulemaking affects how transparent elections are and how political money is tracked, with disputes often centred on speech, disclosure, and enforcement consistency.
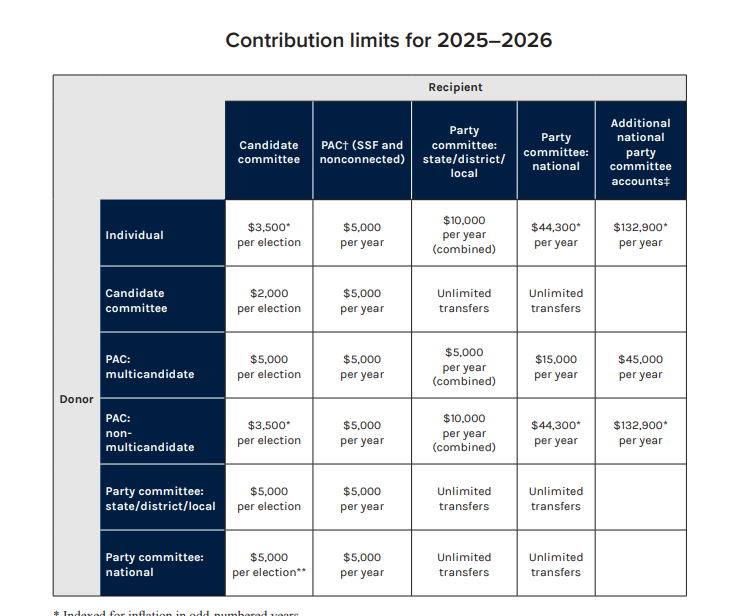
This FEC table summarizes contribution limits for the 2025–2026 federal election cycle by donor type and recipient type. It exemplifies how election regulators operationalize broad statutory goals (prevent corruption; promote transparency) into specific, enforceable numerical limits. Students can use it to connect campaign-finance debates to concrete compliance rules. Source
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): financial markets and investor protection
The SEC regulates securities markets to promote fair dealing and protect investors.
Policy areas commonly shaped by SEC rules:
Disclosure requirements for public companies (what must be reported and how)
Market conduct rules for brokers, exchanges, and investment advisers
Anti-fraud enforcement standards and compliance obligations
SEC rules demonstrate how regulation can influence business behaviour by changing incentives, information requirements, and penalties for misconduct.
What to remember for the exam
These agencies regulate different policy areas: DHS (security/immigration), DOT (transport safety), VA (veterans’ benefits/services), Education (federal education programme compliance), EPA (environment), FEC (campaign finance), SEC (securities markets).
Agency discretion is most visible when rules define the practical meaning of broad statutory phrases like “reasonable,” “safe,” or “adequate.”
FAQ
They are typically structured to reduce direct presidential control (e.g., multi-member leadership), which can affect enforcement priorities and the pace of issuing rules.
Regulations are legally binding rules. Guidance explains how an agency interprets or plans to enforce rules, but usually has less direct legal force.
They can impose broad compliance obligations across industries and states, raising disputes over costs, scientific assumptions, and how strict standards should be.
Yes. Transportation-related pollution can involve both safety/transport administration and environmental standards, creating coordination challenges and shared policy influence.
They alter required reporting and liability exposure, encouraging internal compliance systems and changing incentives about what risks firms reveal to investors.
Practice Questions
Identify two federal agencies that exercise rulemaking discretion and state one policy area regulated by each. (2 marks)
1 mark: correctly names an agency from the list (DHS, DOT, VA, Education, EPA, FEC, SEC) and matches it to an accurate policy area.
1 mark: repeats with a second correct agency-policy match.
Explain how rulemaking by the EPA and the SEC can shape public policy outcomes, using one specific type of regulation for each agency. (6 marks)
1 mark: explains that EPA rulemaking creates enforceable environmental standards.
1 mark: provides a specific EPA regulation type (e.g., emissions limits; air/water quality standards; hazardous waste rules).
1 mark: links EPA rules to policy outcomes (e.g., compliance costs, pollution reduction, enforcement).
1 mark: explains that SEC rulemaking creates enforceable market/investor protection requirements.
1 mark: provides a specific SEC regulation type (e.g., corporate disclosure rules; market conduct rules; anti-fraud compliance requirements).
1 mark: links SEC rules to policy outcomes (e.g., transparency, investor protection, market behaviour).

