AP Syllabus focus:
‘Liberal ideologies generally support more national government involvement in social issues such as education and public health, leaving less responsibility to state governments.’
Liberal perspectives on social issues emphasise using federal power to expand access, protect rights, and reduce inequality. This approach typically views national standards and funding as necessary to ensure fair treatment across states and communities.
What “liberal views” imply for social issues
Liberalism in U.S. politics usually prioritises equal opportunity, civil rights, and government action to address social and economic inequality. Applied to social issues, this translates into support for more national government involvement rather than leaving policy mainly to the states.
Core idea: federal responsibility for baseline protections
Social policy: Government decisions and programmes that shape access to services and quality of life, including education and public health.
A liberal view often treats education and health as areas where outcomes should not depend heavily on geography, local tax bases, or state-level political preferences.
Why liberals favour national government involvement
Ensuring uniform access and equity
Liberals argue that state-by-state control can produce uneven outcomes and widen disparities. Greater federal involvement is seen as a way to:
Set minimum national standards (for safety, access, and nondiscrimination)
Reduce inequalities tied to income, race, disability status, immigration status, or ZIP code
Protect minority rights when state majorities might limit them
Addressing collective action problems
Liberals also frame education and public health as problems that cross borders and require coordination.

This organizational chart maps the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and its major offices and national centers. It illustrates how federal public health capacity is structured to coordinate surveillance, preparedness, and disease control across the country, reinforcing the idea that some health threats are not confined to state borders. Seeing the hierarchy also helps explain why liberals often argue that national institutions can set priorities and mobilize resources at scale. Source
Disease outbreaks, environmental health risks, and insurance markets can span multiple states.
Education quality affects national economic competitiveness and civic capacity.
How liberals translate preferences into policy
Federal spending and program design
A common liberal approach is to expand or protect federal programmes and funding streams, often targeting underserved groups.
Grants-in-aid can direct resources to districts, hospitals, and communities with greater needs.
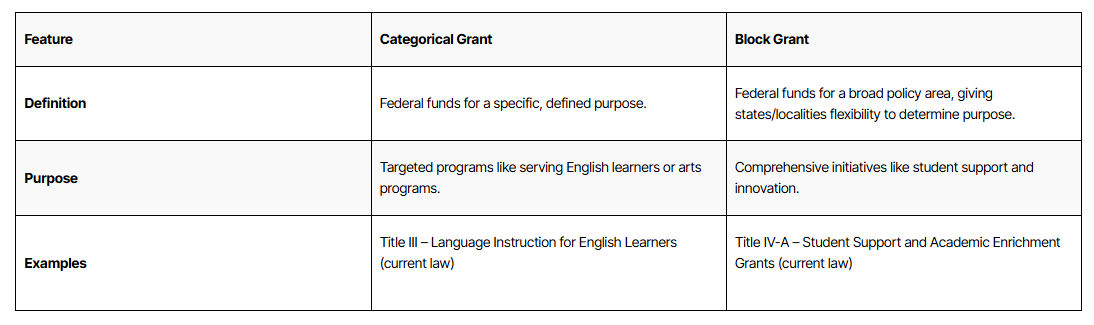
This table contrasts categorical grants and block grants across key features (definition, purpose, and examples). It helps connect federal spending tools to policymaking strategy: categorical grants typically increase federal direction through more specific purposes, while block grants increase state/local discretion within a broad policy area. The comparison makes it easier to see how liberals can favor federal funding while still debating how many “strings” should be attached. Source
Eligibility expansions and subsidies are used to broaden coverage and participation.
Regulation and standards
Liberals tend to support national rules that require institutions receiving federal support to meet certain obligations.
In education, standards may focus on nondiscrimination, accommodations, and access.
In public health, standards may address preventive care, consumer protections, and safety.
Rights-based framing
Liberal arguments frequently connect social policy to constitutional and legal commitments to equal protection and due process, viewing federal involvement as a safeguard when state policies produce exclusion or unequal treatment.
Education: typical liberal priorities
In education, liberal views generally support:
Increased federal investment to promote equal opportunity
Policies aimed at reducing achievement gaps and improving access for disadvantaged students
National enforcement of civil rights protections in schools
Liberals often see education funding as a tool to offset unequal local revenue (for example, reliance on property taxes), which can make school quality vary sharply across communities.
Public health: typical liberal priorities
In public health, liberal views commonly support:
Broader access to affordable healthcare through federal involvement
Stronger national capacity for emergency preparedness and disease control
Federal action to reduce health disparities across regions and demographic groups
Public health is often treated as a national interest because individual decisions (vaccination, preventive care, workplace safety) can create spillover effects for the wider population.
Key tensions liberals accept (and how they respond)
Even while favouring national involvement, liberals recognise trade-offs and typically respond by arguing that:
Federal action can be designed with flexibility for local conditions while still maintaining national protections.
National programmes can be evaluated and adjusted to improve effectiveness and fairness rather than abandoned in favour of state control.
Democratic accountability exists through elected federal institutions and transparency requirements tied to federal funding.
FAQ
They often look to whether unequal access undermines equal citizenship and opportunity.
They may argue “rights-like” treatment is warranted when denial produces systematic exclusion or discrimination.
Commonly cited evidence includes:
Persistent interstate disparities in outcomes
Discrimination patterns not addressed by states
Cross-border spillovers (e.g., communicable disease impacts)
They may accept mixed delivery models but prioritise public standards.
The key concern is whether private participation expands access without weakening accountability or equity.
They often favour baseline requirements paired with flexibility in implementation.
They may support pilot programmes, waivers, or targeted grants to test local innovations within national goals.
They may argue long-term savings from prevention and improved opportunity.
They may also prioritise targeted funding, cost controls, or revenue increases to finance expansions more sustainably.
Practice Questions
(2 marks) Describe one reason why liberals generally support more national government involvement in education or public health.
1 mark: Identifies a valid reason (e.g., reducing inequality, ensuring uniform access, protecting rights).
1 mark: Briefly explains how national involvement helps achieve that aim.
(6 marks) Explain two ways liberal ideologies support increased national government involvement in social issues such as education and public health, and explain one likely consequence of this approach for policy outcomes.
1 mark: Identifies first way (e.g., federal funding/grants, national standards, rights enforcement).
1 mark: Explains first way in context of education/public health.
1 mark: Identifies second way (must be different from the first).
1 mark: Explains second way in context of education/public health.
1 mark: Identifies a likely consequence (e.g., more uniform access, reduced state discretion, expanded services).
1 mark: Explains the consequence clearly linked to increased national involvement.

